Stable Isotopes in food web studies
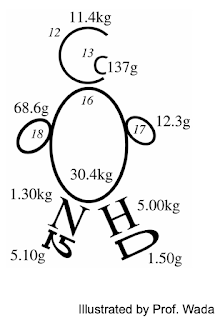
Stable Isotope Isotope is defined as elements with same atomic number (= same number of protons) and different neutron number. Therefore, isotopes of an elements have different mass. For example, 12 C, 13 C and 14 C are all carbon isotopes and 13 C and 14 C are heavier isotopes than 12 C Stable isotopes are isotopes which is stable without radioactive decay. 14 N is a radioactive isotope emitting radioactive radiation, eventually collapsing into 14 N while 13 C is a stable isotope which remain stable in nature. Usually, heavier stable isotopes exist in very little amount in nature. In a person of 50 kg, 13 C weighs only 137g while 12 C does 11.4 kg. For nitrogen, 15N weighs only 5.1 g while 14N does 1.3 kg. Fig. 1. An 'isotope man' illustrated by Prof. Eitaro Wada. http://www.lowtem.hokudai.ac.jp/isophysiol/pg39.html Most studied isot...